Definition of ecosystems – Before we discuss further about ecosystems, we first need to know about the meaning and understanding of ecosystems. With this understanding, it is hoped that it will be easier and faster for us to understand the reviews and descriptions of the ecosystem itself.
Ecosystem is an ecological system (interaction) that is formed mutually between living things and their environment. It can also be said that the notion of an ecosystem is a unity of living things in one place that has mutual influence between one another.
An ecosystem is something that is different from one another, for example a coastal ecosystem, this is a unity of living things on the beach that need or influence each other. There are marine ecosystems, river ecosystems, lake ecosystems, brackish ecosystems, forest ecosystems and others.
So, in an ecosystem has different inhabitants from one another. In this article we take a look at an overview of the ecosystem and its components. But beforehand, we first look at the notion of ecosystem based on expert opinion.
Understanding Ecosystems According to Experts
Ecosystems have links and relationships and are part of an environment. The definition of ecosystem also varies, but all of them have similarities and almost the same substance. Here we see the understanding one by one based on the opinion of experts.
1. A.G. Tansley (1935)
He said that an ecosystem is a unique ecology in that the unit has a function as well as a structure. The meaning of the structure in the unit is that there is a diversity of species.
If the species are increasingly varied or have a high level of diversity, it is called a complex structure. While the meaning of FUNCTION in the ecosystem is something related to energy, the material cycle of the components of the ecosystem.
2. According to Woodbury (1954)
Next, take a look at what ecosystems mean from Woodbury’s view. He said that the ecosystem is a complex unity in an area where there are habitats, plants and animals. referred to as a unique whole unit. This means that everything can be part of the cycle of energy and matter flow.
3. According to the 1997 Environmental Law
The definition of ecosystem according to the Environmental Law of 1997 is an order of necessity in a way that is formed so intact and universal (comprehensive) between all species in the environment that influence each other. Environmental elements can be either biotic or abiotic components.
So, the whole is structured and cannot stand alone, cannot live alone, everything is interdependent, interacts with each other and cannot be separated.
4. According to Odum (1993)
Ecosystem according to Odum is a set of functional units found in an ecology which includes organisms and the environment. The purpose of the environment is abiotic and biotic, where everything is interrelated and dependent.
5. According to Soemarwoto
The definition of ecosystem according to Soemarwoto is an ecological system that occurs and is formed by a reciprocal relationship between living things and their places of residence.
An organization in an ecosystem is called a system because it consists of well-organized components and functions. Each component in it can make a reciprocal relationship.
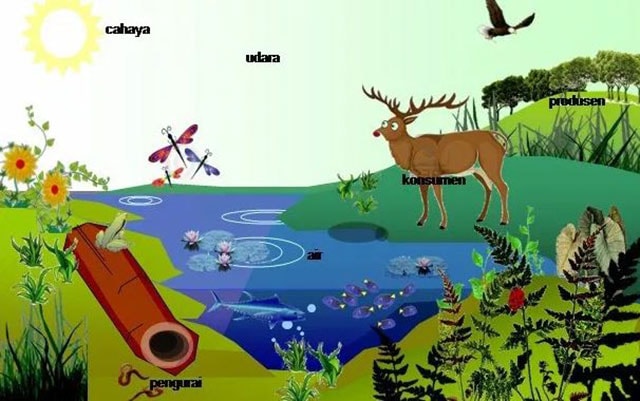
Ecosystem Components
The Ecosystem components are elements that make up the ecosystem that cannot be separated from the ecosystem itself. If not, then the ecosystem is not formed. Well, this means that every time we say an ecosystem, of course there are constituent components in it so that an ecosystem is formed. These components consist of living components and non-living components.
Also see: Types of Environmental Pollution and Examples
The two components of this ecosystem are also called the biotic component and the abiotic component. Biotics are living components and abiotics are non-living components. Then, each of these components has a different occupant too. Here we look at a clearer explanation.
1. Biotic components
The purpose of the biotic component is the part of the ecosystem which consists of living things or living things. Biotic itself means “life”.
An ecosystem will not exist without living things in it. The reason is because these living things need a food chain that will process the surrounding nature to form a food chain.
From this we understand that the biotic component is very important in an ecosystem because without it, an ecosystem will not be formed. Because the cause of the formation of an ecosystem is the presence of a food chain and this is formed from the biotic environment or biotic components.
Some examples of biotic components are humans, plants, animals and microorganisms or decomposing creatures. Let us look at the description of examples of biotic components.
1. Autotrophic organisms or producers
Autotrophic organisms are components of the ecosystem which are also known as percentages. They can produce their own food and even make food for other creatures. The way of making food is by absorbing inorganic compounds and substances and turning them into organic through a performance called photosynthesis.
2. Heterotrophic or consumer organisms
Examples of components of the next biotic ecosystem are heterotrophic organisms or what are called consumers. This is different from organisms that can make their own food. Heterotrophic organisms cannot make their own food, even they are food for their own needs.
So, where will they get their food? Heterotrophic organisms will get food from producers or autotrophic organisms, even some of them will prey on each other who are heterotrophs. The conclusion is that terotrophic organisms take advantage of autotrophic organisms as food and energy sources to survive.
Read also: Lightning Protection: Five Important Things to Know
Examples of heterotrophic organisms are humans and animals or are called all eaters or omnivores and there are also plant or herbivore eaters and meat eaters called carnivores.
3. Decomposers or decomposers
Decomposer organisms or decomposers are the next type of organisms that exist in an ecosystem. Their job is to break down the remains of living things that have died either from heterotrophs or autotrophs.
In short, they are decomposers or decomposers are living things or organisms that convert organic matter into inorganic through a process called decomposition.
The role of decomposers or decomposing organisms is very important in the survival of living things because they are the ones who cause an unbroken food chain. Examples of decomposing organisms are algae, bacteria, fungi, worms, and others.
2. Abiotic ecosystem components
This is the second component that makes up the ecosystem of living things. If the meaning of the biotic component is living things, then the meaning of the abiotic component is the inanimate component.
Also read: Organic and Inorganic Waste
Abiotic components are inanimate elements or components (inanimate objects) that are in the ecosystem and they also affect the survival of living things.
Examples of components of the abiotic ecosystem are temperature, water, sunlight, air, wind, and humidity and others.
That is the understanding of the ecosystem, the components that compose it and the explanation of each and examples of the components that make up the ecosystem.
Read more: Distance Between Earth and Moon