Human blood vessels are very complex and are very long when lined up in a straight line. For blood vessels in humans that are not shaped like that, you can imagine that if they are straight, they are said to be two and a half times the rotation of the earth. Shocking isn’t it? The human blood vessels if all straightened out and put in an elongated way, can reach 10,000 km in length.
This is very extraordinary isn’t it, but the blood vessels of the human body are not elongated like that but rather have branches. This can also be said to be a miracle in human creation.
Also read; Human Respiratory System: Image
Knowing Blood Vessels in Humans
The blood vessels in some people are visible, especially in white people, we can see the blue veins, it is human blood vessels, only a small part of which is still very large and can even be millions of others that are small and invisible to the eye. These blood vessels are shaped like pipes that carry water to various places. Likewise, blood vessels in humans are in charge of circulating blood to all parts of the body.
The blood vessels in the human body are divided into three types, namely arteries (arteries), veins (veins), and capillaries. So, what is the meaning of each of these blood vessels? Come on, let’s look at the explanation below.
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood out of the heart, while Bali veins are vessels that carry blood back to the heart.
Meanwhile, capillaries are blood vessels that function as a place for the exchange of substances such as carbon dioxide, nutrients, oxygen, metabolic waste to chemicals in the body.
The circulatory system in humans is the way blood passes through these blood vessels. blood vessels can be likened to roads and blood is the car, now will everything be smooth if the blood vessels are healthy, not necessarily! We need a place to stop as well as on the highway, now there are organs in the human body that function as a transit point for blood, in this case the heart.
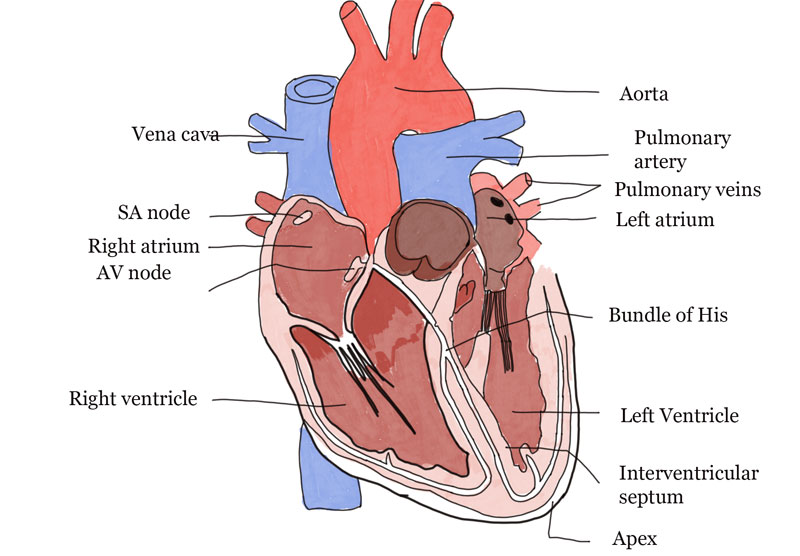
The heart is the most important organ in maintaining smooth blood flow throughout the body, the heart always beats whether we are awake or sleeping even when the heart is out of the human body. It will also always beat unless someone has died.
So, how can the heart always pump blood, the answer is because the heart has four (4) rooms or 4 chambers in it. So, the blood flow in our bodies varies, for example, blood that contains carbon dioxide is pumped through a different route to blood that contains oxygen, this does not mix because if there is a mixture it can be dangerous for our health.
Well, these chambers in the heart regulate it so that all the blood is pumped through their respective paths.
Circulatory (systemic)
After we know the organs that play a role in blood circulation in humans, we now look at the types of blood circulation. There are two blood circulation in humans, some are called the large or systemic blood circulation, and there is a small or pulmonary circulatory system.
Also read: Human Anatomy: Systems and Structure
The large circulatory system (systemic) starts with oxygen-containing blood, this is pumped by the left ventricle of the heart through the circulation and to the rest of the body. Furthermore, the blood in the body that is no longer oxygenated and contains Co2 is returned to the right atrium of the heart by the superior vena cava (for the upper body) and by the inferior vena cava (for the lower body).
Put simply, that great blood circulation through the heart >> the whole body >> the heart.
Small or Pulmonary Circulatory
Pulmonary circulation is different from the large or systemic circulation, if the large blood circulation covers the whole body, then the small blood circulation includes only the lungs. You see, the blood containing carbon dioxide in the right ventricle of the heart is pumped to the lungs. In the lungs, there is diffusion or gas exchange, carbon dioxide is converted into oxygen. When the blood has left the lungs, the blood is then flowed by the pulmonary veins to the left atrium of the heart.
Simply put, this, the small circulation is small is through the heart >> lungs >> the heart.
See: The Human Digestive System
That is how the circulatory system in the human body works as well as the organs that contribute to blood circulation. Hopefully it can add to our knowledge of the circulatory system or blood circulation.